Occupational (Work-Related) Asthma
General Information About Work-Related Asthma
There are hundreds of known causes of work-related asthma. Each year in Michigan, about 80 new cases of asthma caused by exposures to substances at work are reported to the MI Dept of Labor and Economic Opportunity (LEO). Inspections at the companies where these people work find large numbers of fellow workers with asthma or breathing symptoms like asthma.
The work exposures may make a person’s existing asthma worse, or cause new asthma either from becoming allergic to a work place substance or from exposure to a high level of an irritant chemical.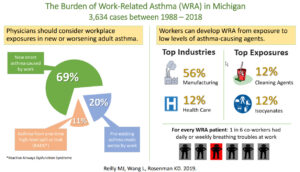
Over 400 substances that can cause asthma in the work place have been identified, and the list continues to grow. Even very low levels of exposure to some of these substances can aggravate or cause asthma. However, employees, employers and health care professionals are often unaware of the association of an individual’s asthma with exposure to substances in the work place.
In Michigan, new cases of work-related asthma are identified in about 80 workers each year; this is an underestimate of the true number of individuals developing asthma from work place exposures in our state. It is estimated there are 228-801 individuals a year who develop work-related asthma in Michigan. Approximately 15-36.5% of adult asthma is considered to be work-related.
A special State tracking program has been identifying individuals with work-related asthma since 1988. The program interviews workers about their work place exposures, their symptoms and the timing of symptoms in relation to work. In some cases, Michigan Occupational Safety and Health Administration (MIOSHA) enforcement officers inspect the work places of the individuals identified in the tracking program. The inspections document exposures, the presence of other symptomatic co-workers, and compliance with Michigan OSHA regulations.
Each year, a summary of the findings from this tracking program is published.
View the most recent Work-Related Annual Report.
Download an infographic from the American Lung Association developed to help workplace administrators become aware of and improve indoor air quality at work.
Here Are A Few Work-Related Asthma Facts
Data from the Michigan Work-Related Asthma (WRA) Surveillance System was analyzed from 1988-2018.
- Overall, the confirmed cases of WRA in Michigan have decreased over the 31 years. The cumulative incidence rate of WRA decreased from 3.5 during 1988-1997 to 2.0 cases per 100,000 Michigan workers during 2008-2018. Surveillance systems in other countries have also reported a downward trend in WRA.
- There were decreases in cases from specific exposures to well-known causes of WRA such as isocyanates and metal working fluids and in the cumulative incidence rate in the overall manufacturing sector (11.6 to 5.6 cases per 100,000 workers). This decrease was consistent with improved workplace engineering and controls such as enclosure of work processes, product substitution and use of personal protective gear.
- However, for cleaning products, which are found across all industries, generally with less standardized work practices than those applied in a manufacturing setting there was an increase over time in the number of cases and percentage of cases associated with cleaning products from 5% to 20%, even before their increased use associated with the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Sixty-six percent of WRA cases had an emergency department visit, with a median of two and an average of five visits, and 35% were hospitalized for their WRA, with a median of one and average of four hospitalizations.
- Despite the high morbidity and cost of WRA, only 49% had applied for workers’ compensation.
- Nine individuals died from an asthma attack from a workplace exposure. The decedents ranged in age from 19 to 77 years. Five were men. Five worked in manufacturing and one each worked in construction, agriculture, food services, and automotive repair. Four were exposed to isocyanates, and one case each was exposed to secondhand cigarette smoke, milk tank cleaning agents, construction chemicals, mold machine release spray, and welding fume.
- WRA cases are useful for targeting workplace enforcement inspections. The confirmed cases worked in 2,601 facilities. Michigan OSHA inspected 806 of those facilities. During the inspections, 10,493 co-workers of the index cases completed a confidential respiratory questionnaire; 1,622 (15%) reported being bothered at work by daily or weekly chest tightness, shortness of breath or wheezing, or having new-onset asthma since beginning to work at the facility. Symptomatic co-workers decreased over time from 18% to 12%.
Read the full article: The Burden of Work-related Asthma in Michigan, 1988–2018
Editorial: Some Progress and Direction in the Prevention of Work-related Asthma
NIOSH Science Blog: The Burden of Work-Related Asthma (Jan. 2020)
Substances at work that can cause asthma, and types of work related asthma
There are 3 types of work-related asthma. Learn more about the types of work-related asthma, and find a list of known substances that can cause asthma.
Myths about work-related asthma
There are some commonly held beliefs about work-related asthma that just aren’t true.
Diagnosing and preventing work-related asthma
Find out how work-related asthma is diagnosed, how it can be prevented, and what can be done about it.
The Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America has developed a useful workplace asthma and allergy assessment tool.
More information about how to screen for work-related asthma
Go to the links page, then click on worksites/employers to find more resources about work-related asthma.
Based on materials reviewed and provided by the Michigan State University Occupational and Environmental Medicine Department, updated 2023.
